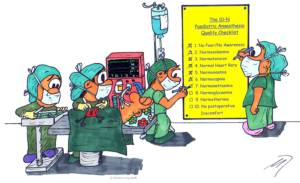
The 10-Ns
Maintenance of physiological homeostasis is key for the Safe Conduct of Anesthesia in Children
The 10-N principles provide a simple matrix of clinical goals.
These principles apply to all pediatric anesthetic procedures from the ‘simple’ to the ‘complex specialist’.
No Fear and No Awareness
Up to 75% of children may experience fear / anxiety during anesthesia, mostly during induction. Learn more about preventing fear…
Accidental awareness is a significant, underreported anesthetic complication. Read on about awareness …
Normovolemia
Maintenance of physiological body fluid homeostasis is important for normal organ function. Deviations from this equilibrium (hypo- and hypervolemia) are commonly encountered in the peri-operative period. Find out more …
Normotension
Deviations from patient specific norms may result in physiologically and clinically relevant impairment of organ and tissue perfusion. Explore the problem …
Normal Heart Rate
Cardiac output and organ perfusion is primarily dependent on the heart rate in young children. Read on …
Normoxemia
Hypoxemia is commonly encountered during pediatric anesthesia. Prolonged hypoxemia may lead to adverse short and long-term outcomes.
Hyperoxemia is iatrogenic and may result in the production of reactive oxygen species affecting normal organ function.
Normocapnia
Blood arterial carbon dioxide tensions are modified during anesthesia. Changes in arterial carbon dioxide tensions significantly affect body homeostasis including the acid-base status, the sympathomimetic tone and organ blood flow. Read more ….
Normonatremia
Plasma sodium is the major determinant of serum osmolality and therefore extracellular fluid volume. It is also a major determinant of neuronal excitability. Acute perioperative changes in plasma sodium concentrations are a leading cause of avoidable morbidity and mortality in children. Learn more about sodium equilibrium …
Normoglycemia
Blood glucose homeostasis is important for ensuring a continuing energy supply and stable plasma osmolality. Small infants have reduced glycogen storage capacity and hence have a limited ability to maintain blood glucose concentrations during periods of fasting. Find out what normoglycemia is about …
Normothermia
The perioperative setting increases the risk of temperature disturbances. Anesthesia impairs the ability to regulate body temperature. Deviation of temperature from the physiological range will impact on cellular function and body metabolism. Changes in body temperature may lead to a variety of multi-organ dysfunction. Explore the concept of normothermia …
No Postoperative Discomfort
No Pain
A large number of children still experience significant pain in the perioperative period. Poor pain control remains a significant problem following hospital discharge. Learn more …
Children undergoing anesthesia and surgery are at high risk for PONV. PONV leads to additional discomfort, morbidity and costs. Find out more about PONV …
No Emergence Delirium
Emergence delirium is common following general anesthesia in young children. Effective recognition and treatment is essential to reduce self inflicted injuries and improve satisfaction of parents and caregivers. Read on ….
Learn about ...
- Rights of the child (10Rs)
- Personal and institutional competence (5Ws)
- Quality and equilibrium (10Ns)
- Crisis situations (10Cs)
- Research
- Quality Improvement
- Parental discussion